
Katsutoshi Ono
Kyoto University, Japan
Title: Theories of on-board hydrogen redox electric power generators for infinite cruising range electric vehicles
Biography
Biography: Katsutoshi Ono
Abstract
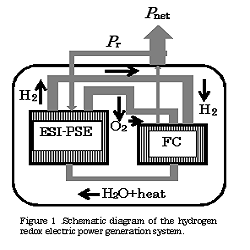
This paper presents the theoretical aspects of a specific propulsion system for electric vehicles, based on a prototype standard passenger fuel cell vehicle (FCV), termed a hydrogen redox electric power generator (HREG). This generator utilizes a combined energy cycle composed of a fuel cell that produces power and an electrostatic- induction potential superposed water electrolytic cell (ESI-PSE) for the synthesis of a stoichiometric H2/O2 fuel for the fuel cell. To allow an essentially infinite cruising range, the fuel must be synthesized while the car is in motion. In this scenario, the HREG offers considerable advantages. Firstly, this device is capable of functioning with zero matter and energy inputs and generates no emissions, without violating the laws of thermodynamics. The H2O → H2 +1/2O2 reduction reaction proceeds in the ESI-PSE, which functions on a so-called “zero power input” mechanism involving the conversion of electrostatic energy to chemical energy. In this unit, the power used is 17% of the total electrical energy that is theoretically required, while the remaining 83% can be provided by electrostatic energy free of power. Part of the power delivered by the fuel cell is returned to the ESI-PSE cell, while the remainder represents the net power output used to drive the electric motor. A second advantage is that the HREG system can be employed on both a large scale, such as in the case of a central power station, and on a much smaller scale, such as for on-board electric power generation in an electric vehicle. The present work performed a theoretical assessment of this new propulsion system for electric vehicles, focusing on the following three aspects:
1. the power electronics circuit connected to the ESI-PSE cell,
2. the performance of the on-board HREG system,
3. the lithium-ion battery charge-discharge reciprocating electric power generator.
Recent Publications:
1. Ono K: (2015) Energetically self-sustaining electric power generation system based on the combined cycle of electrostatic induction hydrogen electrolyzer and fuel cell IEEJ, Trans. on Fundamentals and Materials, Vol.135 No.1 pp. 22-33.
2. Ono K: (2016) Hydrogen redox electric power and hydrogen energy generators, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, vol.41 PP.10284-102913.
3. Ono K: (2016) “Hydrogen redox electric power and hydrogen energy generators”, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, vol.41 P.10284-10291
4. Barbir F, PEM fuel cells, Theory and Prracice, Elsevier, Amsterdam P.268..
5. Annual Report, National Resources and Energies 1999/2000, The Agency for Resources and Energies, Japan.
6. O’ Hayre R, Cha S.W, Collela W and Prinz F.B., (2006) Fuel cell, Fundamentals, John Wiley & Sons INC.

