
Mamta Kumari
Homi Bhabha National Institute, India
Title: Fuel cell performance of SPEEK-PEG-PWA composite membrane
Biography
Biography: Mamta Kumari
Abstract
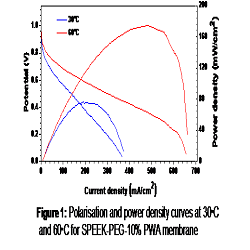
Proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is promising technology for clean and efficient power generation in the 21st century. Currently perfluorinated membranes are used as electrolyte that have high cost and complicated synthesis process which limits the commercialization of the PEMFC. Hydrocarbon polymers are good alternative for membranes and during last few decades research has been concentrated on that. The present work focuses on the development of composite membrane by using a thermoplastic polymer, partially sulfonated polyether ether ketone (SPEEK) and polyethylene glycol (PEG) as cross-linker along with varying amount of phosphotungstic acid (PWA) as an inorganic additive. The membranes are prepared using sulfonated PEEK with an ion exchange capacity of 2 meq/g and 33% of PEG having molecular weight of 600 Da was used as cross linker, the amount of PWA was varied from 5 to 50%. Among the various concentration of PWA in membranes, the 10 wt% PWA gave highest conductivity (90 mS/cm), less swelling and good stability in water up to 60ºC. The fuel cell performance of these membranes was measured using a 25 cm2 membrane electrode assembly made using commercial carbon paper based electrode (0.2 mg/cm2 Pt loading). The cell performance tests were carried out (H2/O2 at 2 bar pressure) at 30 and 60ºC (Figure 1). The maximum power density obtained at 30ºC was 75 mW/cm2 at current density of 200 mA/cm2 and voltage 375 mV which increased at 60ºC to 173 mW/cm2 at current density of 440 mA/cm2 and voltage 400 mV. The cell gave stable performance after running for 40 hours at its maximum power. The present membrane performance is comparable with the reported value for commercial membranes (power density of 360 mW/cm2 to 420 mW/cm2 at 600 mV and 80ºC). Hence, the SPEEK-PEG-PWA membranes can be an alternative solid polymer electrolyte for fuel cell.
Recent Publications:
1. Yee R S L, Rozendal R A, Zhang K, Ladewig B P (2012) Cost effective cation exchange membranes: A review. Chemical Engineering Research and Design 90:950-959.
2. Sambandam S, Ramani V (2007) SPEEK/functionalized silica composite membranes for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources 170:259-267.
3. Moreno G N, Molina C M, Gervasio D, Robles P F J (2015) Approaches to polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and their cost. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 52:897-906.
4. Lee H K, Chu Y J, Kim R A, Nahm S K, Kim J C, Yoo J D (2013) Densely sulfonated block copolymer composite membranes containing phosphotungstic acid for fuel cell membranes. Journal of Membrane Science 434:35-43.
5. Colicchio I, Wen F, Keul Helmut, Simon U, Moeller M (2009) Sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)-silica membrane doped with phosphotungstic acid. Morphology and proton conductivity. Journal of Membrane Science 326:45-57

